

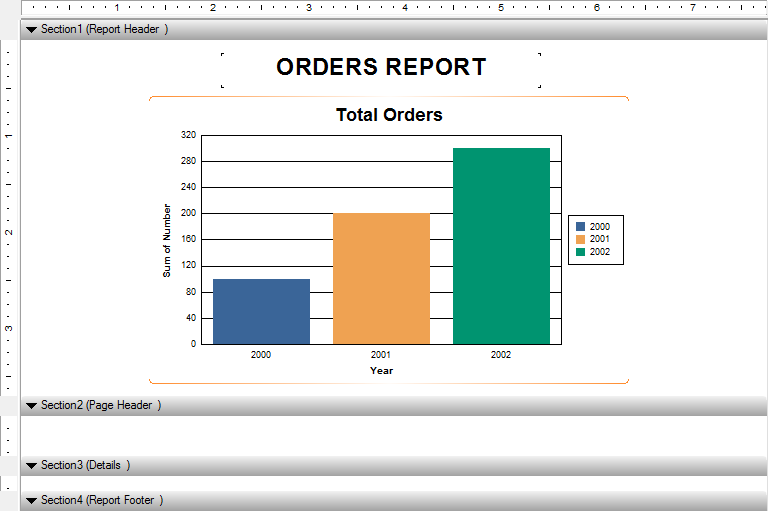
The tail: augmentation by venous return.The investigators assessed the reliability of UnGraph by comparing data extracted by two independent coders for each of 91 published graphs.
#Graphclick for windows windows
#Graphclick for windows software
Gas Man® software includes a printed tutorial with a comprehensive set of examples. Click below to see samples of these screeens, annotated with more information about the program. The Gas Man® software is organized around two main screens - the Picture and the Graph. Gas Man® is used by hundreds of practicing anesthesiologists and dozens of medical and veterinary teaching programs around the world. Gas Man® is the answer: for teaching, experimenting and planning anesthesia administration on the computer, before trying it in the OR. And for clinical and economic reasons, it is increasingly important for the anesthesiologist to seek the most effective and least costly combination of agents and administration techniques. This is particularly true now that new agents are available for use in the OR. Anesthesia uptake and distribution is one of the most challenging subjects in anesthesiology to learn and to teach. It shows the time course of anesthesia uptake in each compartment of the body – lungs, heart, brain – as well as the breathing circuit and vaporizer. The Gas Man® computer model graphically simulates the pharmacokinetics of anesthesia administration. Each concept taught by Gas Man® is fully documented and further explained in the tutorial. It combines an award-winning tutorial text with powerful, easy-to-use software. If nothing is selected, a description of the window at the root of the graph is shown.Gas Man® is a unique computer tool for teaching, simulating and experimenting with anesthesia uptake and distribution. The Description: are gives a description of the item selected in the Graph: area. See 27.3 Performing operations on windows for details.
If no items are selected, the commands in this menu apply to the root window of the graph. To make one of the child windows be the root of the graph, select it and choose Works > Windows > Browse - Window.Īny items selected in the graph can be operated on using commands in the Works > Windows menu. To see the children of an unexpanded node in the graph, click on the unfilled circle to its right. Select any item in the graph to display its description in the Description: area. A graph of the parent window together with its children - each individual window that has been created - is drawn in the main area. When you first create a Window Browser, it automatically browses the parent window of the whole environment. The generic facilities available to all graphs throughout the LispWorks IDE are available here see 6 Manipulating Graphs for details. Although our analysis only required the y-axis values, GraphClick can also be configured to extract precise x-values (e.g., as in a scatter plot). The window graph displays the current window and all its subwindows. As a result of the method described in those latter steps, y-values were calculated automatically by GraphClick by transforming the vertical position of the cursor when coders clicked on each data point. The Graph: text box shows the window object that is being examined that is, the window at the root of the graph.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
